Bayesian Prediction for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
This project predicted breast cancer diagnosis using selected cell nuclei characteristics and compared Bayesian and Frequentist frameworks. Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) Data Set was used, including diagnosis (malignant or benign) and 30 cell nucleus features. The study focused on the first 10 features due to multicollinearity concerns.
The Bayesian approaches included stochastic search variable selection (SSVS) and Bayesian lasso for variable selection, and Bayesian logistic regression model for model construction.
The Frequentist approaches included principal component analysis (PCA) to select variables and used a regular logistic regression model to fit data.
Three combinations of variable selection and models were compared:
SSVS + Bayesian Logistic Regression:
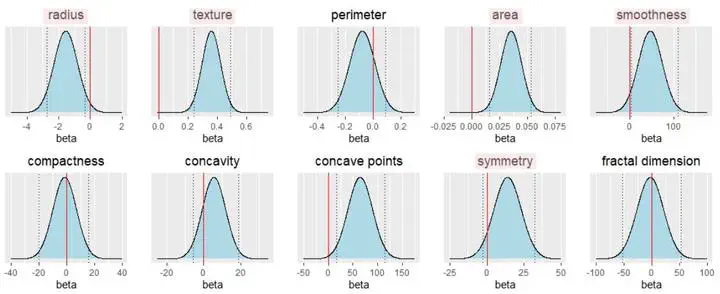
- Selected predictors: texture, smoothness, compactness, symmetry, fractal dimension.
- Test error rate: 0.091.
Bayesian Lasso + Bayesian Logistic Regression:
- Selected predictors: radius, texture, area, smoothness, concave points.
- Test error rate: 0.056.
PCA + Frequentist Logistic Regression:
- Selected predictors: concave points, fractal dimension, texture.
- Test error rate: 0.070.
The codes and detailed documents can be retrieved via my GitHub Repo.